Web 3.0 (Web3) is the third generation of the evolution of web technologies. The web, also known as the World Wide Web, is the foundational layer for how the internet is used, providing website and application services.

First, let’s make the difference between 2.0 and 3.0 clear.
so, what Are Web 2.0 and Web 3.0?
Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 refer to successive iterations of the web, compared with the original Web 1.0 of the 1990s and early 2000s.

Web 2.0 is the current version of the internet (a term often used interchangeably with the web) with which we are all familiar, while Web 3.0 represents its next phase.
Web refers to the World Wide Web (WWW), the internet’s core information retrieval system. The WWW initialism used to (and often still does) preface a web address and was one of the first characters typed into a web browser when searching for a specific resource online. Internet pioneer Tim Berners-Lee is credited with coining the term World Wide Web to refer to the global web of information and resources interconnected through hypertext links.
And here is Web 1.0 for some added context.
Web 1.0

Berners-Lee pioneered the early development of the internet in 1990 when he was a computer scientist at European researcher CERN. By October 1990, Berners-Lee had written the three fundamental technologies that became the foundation of the web, including the very first webpage editor/browser (WorldWideWeb.app):
HTML: HyperText Markup Language, the markup or formatting language of the web
URI or URL: Uniform Resource Identifier or Locator, a unique address used to identify each resource on the web
HTTP: HyperText Transfer Protocol, which allows for the retrieval of linked resources from across the web
Defining Features of Web 3.0
- Decentralized. As opposed to the first two generations of the web, where governance and applications were largely centralized, Web 3.0 will be decentralized. Applications and services will be enabled in a distributed approach, where there isn’t a central authority.
- Blockchain-based. Blockchain is the enabler for the creation of decentralized applications and services. With blockchain, the data and connection across services are distributed in an approach that is different than centralized database infrastructure. It can also enable an immutable ledger of transactions and activity, helping to provide verifiable authenticity in a decentralized world.
- Cryptocurrency-enabled. Cryptocurrency usage is a key feature of Web 3.0 services and largely replaces the use of fiat currency.
- Autonomous and artificially intelligent. More automation overall is a critical feature of Web 3.0, and that automation will largely be powered by AI.
What is Web 3.0 in crypto?
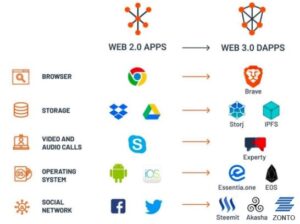
When it comes to Web 3.0, you’ll find that cryptocurrency is frequently mentioned. This is because many of the Web 3.0 protocols rely heavily on cryptocurrencies. Instead, it offers a monetary incentive (tokens) to anyone who wishes to help create, govern, contribute to or improve one of the projects. Web 3.0 tokens are digital assets that are associated with the vision of creating a decentralized Internet. These protocols may provide various services, such as computation, bandwidth, storage, identification, hosting and other online services formerly provided by cloud providers.
For instance, the Livepeer protocol, which is based on Ethereum, provides a marketplace for video infrastructure providers and streaming applications. Similarly, Helium incentivizes consumers and small businesses to supply and confirm wireless coverage and send device data through the network using blockchains and tokens.
What’s a Real-World Example of How Web 3.0 Will Be Able to Provide Greater User Utility?
For example, if you are making plans for a vacation and are on a budget, you currently would have to spend hours looking for flights, accommodation, and car rentals, trawling through numerous websites and comparing prices. With Web 3.0, intelligent search engines or bots will be able to collate all this information and generate tailored recommendations based on your profile and preferences, saving you hours of work.






